Amoled is not a backlight _amoled detailed (principle, structure, process flow)
AMOLED (AcTIve Matrix/Organic Light EmitTIng Diode) is an active matrix organic light emitting diode panel. Compared with traditional liquid crystal panels, AMOLED has the characteristics of faster response, higher contrast, and wider viewing angle.
In AMOLED, OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) describes a specific type of thin film display technology - organic electroluminescent display, and AM (Active Matrix) refers to the pixel addressing technology behind it. As of 2011, AMOLED technology has been used in mobile phones and media players, and continues to move toward low power, low cost, and large size.
The AMOLED displays light that is previously stored or integrated into the TFT after being electrically excited by the OLED matrix molecules, and acts as a set of switches to control the flow of current to each pixel. TFT backplane technology is the key to making AMOLED displays. Today, two major TFT backplane technologies, polysilicon and amorphous silicon, have been used in AMOLEDs.
The advantages of AMOLED are self-luminous, wide viewing angle, and high pair. Compared with passive OLEDs, AMOLEDs have higher refresh rates and significantly lower power consumption, making AMOLEDs ideal for use in power-sensitive portable electronic devices. The disadvantage is that AMOLED displays can be difficult to see in direct sunlight.

Each pixel of the AMOLED liquid crystal screen can self-illuminate, so no backlight is needed, so the AMOLED screen is relatively power-saving than the TFT screen. However, because of the pixel arrangement, the resolution of the AMOLED screen is lower than the nominal, so the display effect at the same resolution is not as delicate as the TFT.
The advantage of the AMOLED screen is that it is fast and relatively power efficient.
The use of AMOLED screens requires attention to the fact that the background is set to dark as much as possible. If a large number of backgrounds using light colors are actually used, they consume more power than TFTs.

1, the principle of light
The OLED device structure is an anode, a metal cathode, and an organic functional layer sandwiched therebetween, exhibiting a sandwich structure. A conventional organic functional layer includes a hole transport layer, an electron transport layer, and an organic light-emitting layer. When a voltage is applied to the OLED device, electrons and holes are injected from the cathode and the anode into the electron transport layer and the hole transport layer, respectively, and electrons and holes are combined in the light-emitting layer to form singlet or triplet excitons. Radiation decay is emitted in the form of photons.
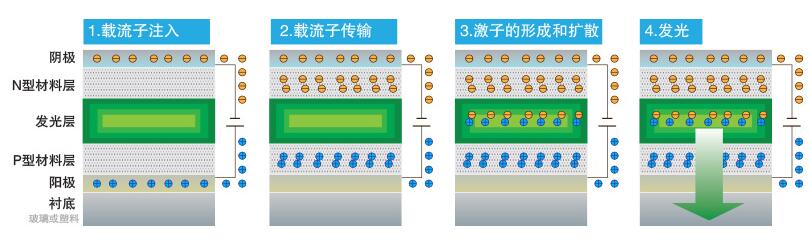
2, the drive mode
The OLED drive mode is divided into passive (PMOLED) and active (AMOLED). The structure of the PMOLED is simple, each pixel is controlled by a separate cathode anode, no additional drive circuitry is required, but too many control lines limit its application to large, high resolution screens. AMOLED drives the LEDs through the driver circuit, minimizing the number of control lines, enabling low power consumption, high resolution, fast response and other excellent optoelectronic characteristics. Therefore, AMOLED has gradually become the mainstream technology of OLED display.
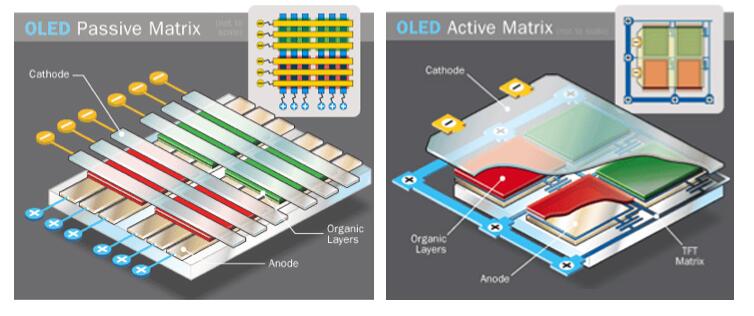
The high-resolution AMLOED drive circuit is getting smaller and smaller, but the corresponding electrical performance requirements are getting higher and higher, so conventional amorphous silicon technology has been difficult to meet new demands. Low temperature polysilicon (LTPS) can meet new development requirements. Its core technology is to form amorphous silicon by "excimer laser crystallization". Low temperature polysilicon has higher carrier mobility, lower defect density, and better electrical properties than amorphous silicon.

The structure of the LTPS-AMOLED and the LCD is basically the same in the structure of the driving circuit, but since the AMOLED is a self-luminous structure and does not require a backlight, it is thinner and lighter. At the same time, due to the characteristics of self-illumination, the power consumption under the dark picture is much lower than the constant power consumption of the LCD backlight, so that the AMOLED display panel has energy-saving characteristics.
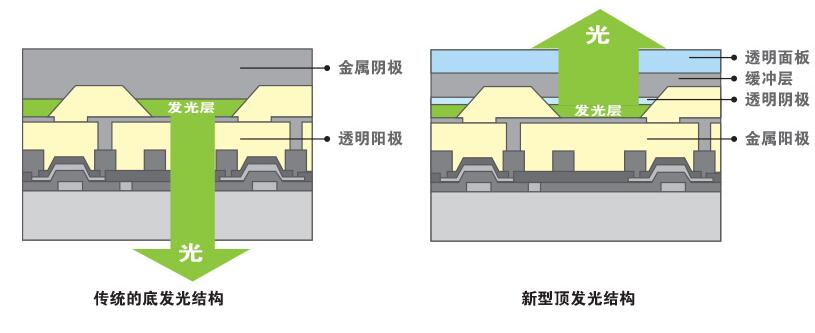
AMOLED also has two structures, bottom light and top light. In the top-emitting structure, the light is not blocked by the driving circuit, and has a higher aperture ratio than the bottom-emitting structure, thereby having a greater advantage in high-resolution applications, and thus has gradually become the mainstream of AMOLED.
MW01 Smart Watch
Mw01 Smart Watch,Mw01 Smartwatch,Smart Watch Mw01,Smartwatch Mw01
everyone enjoys luck , https://www.eeluck.com