Brief Introduction of Radio Frequency Technology and Its Application in Library
As an automatic identification technology, bar code technology has the characteristics of low cost and simple operation. It has been widely used in libraries and other industries, but it also has limitations. For example, data must be collected manually by means of reading and writing devices. Often due to bar code, reader quality misunderstanding and refusal. In recent years, the rapid development of radio frequency identification (RFID) technology not only has the function of bar code technology, but also overcomes its limitations, and is more simple and efficient for the identification of books and materials. This article provides a brief introduction to RF technology and discusses its application in library work.
An RFID overview1 Principle of radio frequency identification
Radio Frequency IdenTIficaTIon is a non-contact automatic identification technology that automatically recognizes and acquires data from stationary or moving objects. It does not require manual intervention and can work in harsh environments.
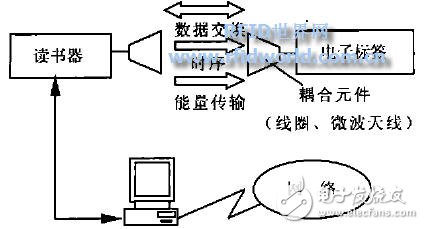
Figure 1 Radio frequency identification system composition diagram
The RFID system is generally composed of an electronic tag (tag), a reader (read2er), and an antenna (Antenna), as shown in Figure 1. The electronic tag is also called a radio frequency tag and a transponder, and is composed of a tag chip and a coupling. Each tag has a unique electronic code and is a data carrier. The electronic tag is attached or embedded on the object to be identified and is used to identify the target object. The antenna is a transmitting and receiving device for data transmission between the tag and the reader. Antennas and readers can be integrated into one unit and exist separately. Different manufacturers have their own integration methods. Any RFID system should contain at least one antenna, either an internal antenna or an external antenna for transmitting and receiving RF signals. The reader is also called a reading device and a scanner. When an electronic tag can wirelessly rewrite data, it is called a reader. A typical reader is composed of a high frequency module (transmitter and receiver), a control unit, and an antenna. In addition, many readers have additional interfaces (RS232, RS485, Ethernet interfaces, etc.) to pass the obtained data to or receive commands from the application system. The API (ApplicaTIon Programm Interface) between the reader and the application system is usually represented by a set of standard interface functions that can be called by development tools (such as VC++, VB, PB, etc.). The functions of standard interface functions generally include the following four aspects:
1) The application system may issue a reader configuration command to the reader as needed.
2) The current configuration status of all possible readers that the reader may return to the application.
3) Various commands that the application system may send to the reader.
4) The result of the execution of all possible commands that the reader may return to the application.
When the RF system is working, the reader sends a certain frequency of the RF signal through the antenna. When the tag enters the magnetic field, the energy is obtained through spatial coupling, and the self-encoded information is sent. The reader obtains the data and decodes it and sends it to the host computer for related processing. In this way, the energy transfer and data exchange are realized according to the timing relationship in the coupled channel, and the identification information can be collected and processed and transmitted remotely through the computer and the computer network, thereby realizing the article. Automatic identification or automatic collection of item information.
2 Classification of RF systems
Usually, the electromagnetic frequency used by the reader to transmit signals is called the operating frequency of the RFID system. The RF system is divided into three types: low frequency (30kHz2300kHz), high frequency (3MHz230MHz) and ultra high frequency (300MHz23GHz) depending on the operating frequency. Common operating frequencies are low frequency 125kHz, 13412kHz and high frequency 13156MHz. The low-frequency electronic tag has a lower cost, but the tag holds less data, has a shorter reading distance, and has a variety of shapes, and the reading antenna is not directional. The high-frequency system label holds a large amount of data, and the reading distance can be several meters to ten meters. It can adapt to high-speed movement of objects, and the shape is generally card-shaped. The reading antenna and the electronic tag antenna have strong directivity and high cost. According to the power supply mode of the electronic tag, the radio frequency system can be divided into an active system and a passive system.
The electronic tag of the active system is equipped with a battery. The energy supplied by the tag battery is partially converted into the RF energy required for the electronic tag to communicate with the reader. The reading distance is long, but the battery life is limited, generally 3 to 5 years. The electronic tag of the passive system does not have a built-in battery. When the reader is outside the reading range of the reader, the electronic tag is in a passive state. Within the read range of the reader, the electronic tag extracts the RF energy obtained from the spatial coupling. The electrical energy required for work. Passive electronic tags generally use reflection modulation to transmit electronic tag information to the reader.
3 Characteristics of RF technology
Since the information transmission medium of radio frequency identification is electromagnetic wave, data can be read and written through external materials, and there is no precise requirement for the distance between the reader and the recognized electronic tag during the information reading and writing process. The electronic tag can work in harsh environments, has a long service life, and can be easily embedded or attached to different shapes and types of products. The electronic tag can write and read data, and the content of the tag can be dynamically changed, and the information storage amount is large. Thanks to the use of anti-collision technology, data interference between tags can be prevented, so the RFID system can process multiple tags at the same time, such as TI's 13156MHz system, which can process about 50 tags per second. The data access of the electronic tag is password protected and requires special equipment for reading and writing, so it is not easy to forge
And change, security is higher.
The application of RFID in library workHigh efficient charging speed for Lenovo and IBM laptop, stable current outlet can offer power for the laptop at the same time charge the laptop battery. The best choice for your replacement adapter. We can meet your specific requirement of the products, like label design. The plug type is US/UK/AU/EU.The material of these products is PC+ABS. All condition of our products is 100% brand new.
Our products built with input/output overvoltage protection, input/output overcurrent protection, over temperature protection, over power protection and short circuit protection. You can send more details of this product, so that we can offer best service to you!
Lenovo Adapter,Charger For Lenovo,Power Supply For Lenovo,Adapter For Lenovo Mini
Shenzhen Waweis Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.laptopsasdapter.com