Competition and risk issues in the design of electrical control loops
Through the case analysis of the competition and risk problems in the electrical control loop, it reveals the concealment and possible consequences of the problem, reminds the electrical practitioners to pay sufficient attention to the problem, sum up the experience in time, improve the design principle, and improve the electrical control system. Reliability of work efficiency and quality.
0 PrefaceIf there is competition and risk in the electrical control loop, it will directly endanger the safety of man and machine, causing major accidents, and the consequences will be disastrous. Therefore, it should be highly valued in the design and application of electrical control loops. In the design of electronic circuits, the issue of competition and risk is in an important position, because the existence of the problem is related to whether the system can work reliably. In addition, because the electrical control of strong electricity is generally intuitive and easy to read, there are few competition and risk issues that are easily overlooked. This problem can occur if the design is poorly designed or the control loop wiring is incorrect during production or overhaul.
1 circuit analysisAfter the soft starter starts the motor bypass operation, the control principle diagram of the motor free stop and delay stop is shown in Figure 1. The start of the motor is realized by the suction of the intermediate relay KA1; after the start speed reaches, the intermediate relay KA2 is closed. The bypass contactor KM is energized and the motor is bypassed. When the SB1 is pressed, the KA2 and KM coils are de-energized and the motor is free to stop. When the SB2 is pressed, the time relay KT coil is energized, and the normally open contact is instantaneously closed and Hold, until the KT's time-delayed normally closed contact opens, the KA2 and KM coils are de-energized and the motor is stopped. The loop has no problem from the control principle, but careful observation will reveal problems with the delay stop loop. If the intermediate relay KA2 and the time relay KT use different types of products (such as one using an electromagnetic relay and the Other as an electronic relay), since the coil operation time is greatly different, KA1 and KT have a problem of grabbing time in the action. That is, when SB2 is pressed, KT is energized and self-sustained, but when the normally closed contact of KT delay is opened, the KT coil is de-energized, the self-locking contact is opened, and the KT delay is normally closed. The point will be closed instantaneously; in the time when the normally closed contact of the KT delay is open from the time delay to the instant closing, if the KA2 is disconnected, the motor can be stopped; otherwise, the motor cannot be delayed (because it has not waited) When KA2 is disconnected, the KT's delay is turned off and the normally closed contact is closed again, causing KA2 to fail to power off). This kind of delayed parking sometimes succeeds and sometimes fails. As a result, the control loop cannot work reliably, which is a typical competition and risk problem. If KT is an electronic time relay (such as ST3PC-D), and KA2 is an electromagnetic intermediate relay (such as JZC3-22d), then, since KT always completes the action first, and KA2 has remanence due to the coil. The release is slow, causing the KA2 to fail to reliably power down. If KT and KA2 are changed to the same type of relay (for example, KT in this example is changed to JSK4-224d), such problems can be solved.
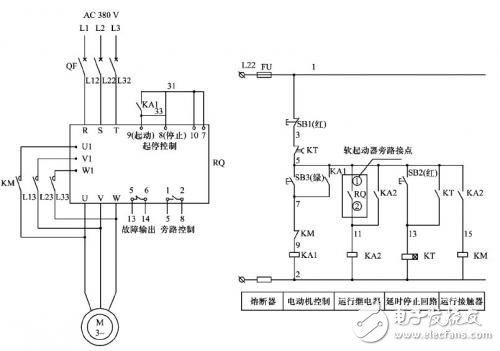
Figure 1 shows the principle of motor free stop and delayed stop control.
Mobile radios,Motorola Two Way Radios,Motorola Talkabout Radios,Motorola Handheld Radio
Guangzhou Etmy Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.digitaltalkie.com