Femto technology and networking application
0 Preface
Femto technology was introduced in 3GPP R8 and became a research hotspot of R8. Because Femto has the characteristics of low transmission power, small coverage, easy deployment, and low price, it has received widespread attention in the industry. Femto uses a fixed broadband access network as the backhaul and provides mobile services to users at the same time. It is a typical fixed mobile convergence technology. Femto will be an important means for full-service operators to provide differentiated services.
For operators, the application of Femto technology can improve indoor coverage quality, improve user experience, and reduce user off-grid rate. At the same time, it can divert macro network traffic at the air interface, ease macro network expansion pressure, and reduce CAPEX and OPEX for 3G network construction. For users, because the cost of Femto deployment is low, operators can provide users with lower communication tariffs. In addition, Femto users can exclusively enjoy wireless resources and transmission resources to obtain better signal quality and access rate, which can promote users Cultivation of data business usage habits. In short, the emergence of Femto technology provides operators with new ideas for indoor coverage.
1 Femto Technology Overview
1.1 Progress of Femto standard
3GPP called Femto as Home Node B (HNB), that is, Home Node B. 3GPP launched related research work on HNB in ​​March 2007, and its goal is to try to form a standard application scenario for home base stations and find a standard solution. In May 2008, 3GPP completed this research work and formed a technical report: TR 25.820 "3G Home Node B Study Item Technical Report (R8)".
R8 regulates the content of HNB architecture, Iuh interface, CSG related identification, measurement rules, cell selection and reselection rules, HNB network management southbound interface, etc. R9 will continue to improve the HNB standard. The work objectives mainly involve the following parts: handover from the macro cell to the HNB cell, handover from the HNB cell to the HNB cell, HNB cells that support OPEN mode and hybrid mode, Uplink multiplexing of CS services on the Iuh interface.
In terms of industry standards, CCSA started the formulation of HNB series industry standards in April 2009. This series of standards includes home base station equipment technical requirements and test methods, home base station gateway equipment technical requirements and test methods, home base station management system equipment technical requirements and test methods, home base station and home base station management system interface test methods, home base station Iuh Interface technical requirements and test methods. At present, the series of standards has been submitted for approval one after another and is in the stage of being released.
1.2 Femto Industry Chain Status
At the same time as the Femto standard was established, the industry also followed up quickly. Huawei, Aran, and Nokia Siemens launched the first batch of Femto solutions in early 2009. By the second half of 2009, Cisco, NEC, and Xinyoutong have launched Own Femto product. From the perspective of the equipment industry chain, Femto technology has matured and has the conditions for large-scale commercial use.
On the commercial side, NTT Docomo, Vodafone, T-mobile and other mainstream operators have carried out related trials. Sprint, Verzion, AT & T are also embarking on Femto trials and commercial preparations, but there is no real large-scale commercial Femto network.
2 Femto key issues
2.1 Network architecture
The Femto access network is mainly composed of HNB, Home Base Station Gateway (HNB GW), Security Gateway (SeGW) and Home Base Station Network Management System (HMS) (see Figure 1). HNB is a user's private device, connected to the HNB GW through the public IP network, and the HNB GW is connected to the core network through the Iu interface. From the perspective of the core network, the HNB access network is the RNC, and the HNB GW accesses the core network through the standard Iu interface; from the UE side, the HNB access network is the Node B, and the HNB and the UE use the standard Uu interface for communication .
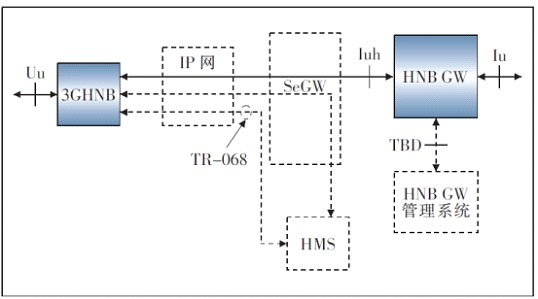
Figure 1 Femto I network structure
HNB has the wireless bearer function of Node B, provides a standard Uu interface to the terminal, and also integrates RNC wireless resource management, mobility management and other functions. HNB also provides the INB interface of HNB GW.
The HNB GW is a new gateway device for the HNB system. It aggregates services from many HNBs, and then passes them back to the existing core network through the standard Iu_CS and Iu_PS interfaces. System characteristics. The HNB GW also has functions such as Iuh link management, UE registration, HNB registration, and UE access control.
HMS mainly provides the network management function of HNB, and TR069 protocol is adopted between HMS and HNB. Specific network management functions include user management, software management, parameter configuration, fault management, performance management, HNB topology management, and log management. HMS also supports the HNB GW discovery function during the HNB initialization process, provides HNB with initial configuration data, performs location information verification on the HNB, and maintains the admission list.
2.2 Self-configuration self-optimization function
Self-configuration and self-optimization are the most important functions of Femto.
On the one hand, Femto has a large number, and operators are inconvenient and unable to invest a lot of energy to open and maintain it, which requires HNB to be plug-and-play and easy to maintain. Plug and play means that Femto automatically completes the process of authentication, network discovery, IP acquisition, IP Sec tunnel establishment, and automatic parameter configuration after powering on. Convenient maintenance means that operators can perform remote batch configuration management, software upgrades, and automatic log storage through OMC.
On the other hand, an important principle of Femto deployment is that it cannot cause great interference to the macro network and cannot cause the quality of the macro network to deteriorate. This requires Femto to have an adaptive self-optimization algorithm to ensure the optimal transmit power to reduce the interference of the Femto network to the macrocell.
In addition, Femto has automatic wireless measurement, automatic neighbor configuration and other functions to meet the mobility management requirements between it and the macro network.
2.3 UE access control
Femto is a user's private device, so access control is required for the terminal. According to different access control strategies, 3GPP divides Femto into three modes, namely closed mode, open mode and mixed mode.
In closed mode, only users of this Femto are allowed to access, and other users are denied access. CSG is the concept of closed user group (introduced in R8), used for access control. According to the terminal's support for CSG, it is divided into non-CSG terminal access control and CSG terminal access control. For non-CSG terminals, that is, terminals that do not support CSG, there will be a user admission list at Femto or Femto GW. If the user's IMSI is in the admission list, they can be accessed, otherwise they are denied access. Access control of non-CSG terminals is done on the access network side, that is, at Femto and Femto GW. For the CSG terminal, see if the CSG of the UE and Femto are the same, if they are the same, the access is allowed, otherwise the access is denied. The access control of the CSG terminal is completed in the core network, so the access control of the CSG mode requires that the terminal, Femto, and core network all support the CSG function.
R9 introduced the open mode and mixed mode. Femto in open mode does not perform access control, and all legal terminals can be accessed. From the perspective of the UE, Femto is a macro base station.
Mixed mode is between open mode and closed mode. Mixed mode Femto belongs to a CSG. With mixed mode Femto, in addition to users in the CSG list, legal users outside the CSG list can also access. However, users in the CSG list have high priority. When resources are limited, the quality of service of users in the CSG list should be guaranteed first.
2.4 Location access restrictions
The location access restriction is to restrict the use of Femto in other places, mainly based on the following considerations.
First of all, protect the operator's long-distance income, because Femto generally uses home access, so if Femto is used in other places, the call to the home location under the Femto will be charged according to the local phone, which will cause the operator to call The loss of income.
Second, prevent Femto from being used in other operator networks.
Finally, because the same operator may have different operating strategies in different regions, market chaos will occur if location access restrictions are not adopted.
3GPP provides three solutions in TS 25.467, which are position binding based on macro network, position binding based on broadband information, and position binding based on GPS. The specific implementation process is not detailed here.
Guangdong Ojun Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.ojunconnector.com