What is the difference between LoRa and NB-IoT? From technology to application comparison LoRa, NB-IoT
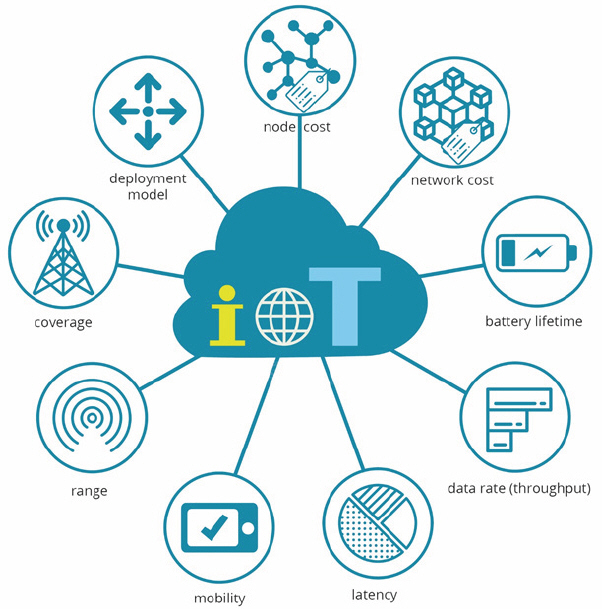
IoT applications need to consider many factors such as node cost, network cost, battery life, data transfer rate (throughput), latency, mobility, network coverage, and deployment type. It can be said that there is no one technology that satisfies all IoT needs. The two technologies NB-IoT and LoRa have different technical and commercial characteristics, so there will be differences in the application scenarios. Here, we will elaborate on the differences between the two, and illustrate their applicable application scenarios.
What are the advantages of NB-IoT?
As a technology applied to low-rate services, the advantages of NB-IoT are not hard to imagine:
• Strong links: In the same base station scenario, NB-IoT can provide 50-100 times more access than existing wireless technologies. One sector can support 100,000 connections, supporting low latency sensitivity, ultra-low device cost, low device power consumption, and optimized network architecture. For example, due to the limited bandwidth, operators only open 8-16 access ports for each router in the home. In a home, there are often multiple mobile phones, laptops, and tablet computers. The need for networking of hundreds of sensing devices has become a thorny problem. The NB-IoT is enough to easily meet the networking needs of a large number of devices in future smart homes.
• High coverage: The indoor coverage of NB-IoT is strong, and its gain is 20dB higher than that of LTE, which is equivalent to 100 times more coverage area. Not only can it meet the demand for a wide coverage in rural areas, but it also applies to applications such as plant sites, underground garages, and well covers that require deep coverage. Take manhole cover monitoring as an example. In the past, the GPRS method needed to extend an antenna, which could easily cause damage to vehicles. However, as long as NB-IoT is properly deployed, it can solve this problem.
• Low power consumption: Low power consumption is an important indicator of IoT applications, especially for some equipment and occasions where batteries cannot be replaced frequently, such as various types of sensing and monitoring equipment installed in remote areas of mountainous wilderness. Once the smartphone is charged on a daily basis, battery life of up to several years is the most essential requirement. NB-IoT focuses on small-data-rate and low-rate applications, so the power consumption of NB-IoT devices can be very small, and the device lifetime can be significantly increased from the past few months to several years.
• Low cost: Compared to LoRa, NB-IoT does not need to be rebuilt, and RF and antennas are basically multiplexed. Taking China Mobile as an example, there is a relatively wide frequency band at 900 MHz. It is only necessary to clear out a portion of the 2G frequency band, and it is possible to directly deploy LTE and NB-IoT simultaneously. Low speed, low power consumption and low bandwidth also bring low cost advantages to NB-IoT chips and modules. The expected price of the module does not exceed $5.
However, NB-IoT still has its own limitations. In terms of cost, the NB-IoT module is expected to fall within 5 US dollars in the future, but currently the price of chips supporting Bluetooth, Thread, and ZigBee is only around US$2. The price of chips supporting only one of the standards is less than 1. The huge price gap will undoubtedly create concerns for companies deploying NB-IoT.
What are the advantages of LoRa?
1, spread spectrum technology, improve the receiving sensitivity (15 km, 10mA receive current, sleep current
2. The air transmission time of the positioning opportunity signal is not the RSSI (Received Signal Strength Index), and the accuracy is 5m@10km. A wide range of positioning instructions rely on GPS to meet the requirements. Small-scale positioning of iBeacon is not worse than it is. If there is no pleasure in both sides, what is the benefit of using it?
3, the most critical is that other technologies have mature applications in mobile phones, if you want to make this new technology rapid development must enter the civilian market, the middle of the degree of difficulty? How much resources do you need to integrate? With Wi-Fi, 3/4G, and Bluetooth, how likely is it to add this technology to mobile handsets?
4. If the home smart device is to choose this technology, it does not see its advantages over zigbee, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi as access interfaces. It does not have strong motivation (technical or cost advantages) to devour existing market share. Difficult to do.
LoRa's direction is basically in industrial applications.
Frequency band, service quality and cost
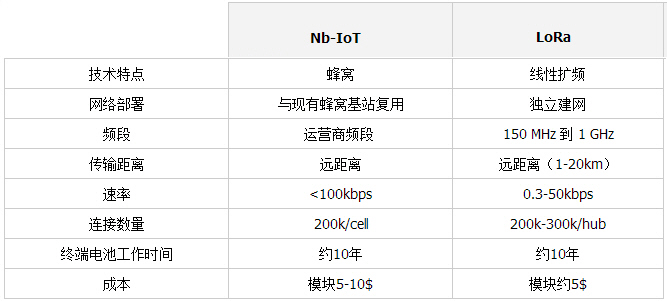
LoRa works in unlicensed bands below 1 GHz, so no additional fees are required for application. NB-IoT and cellular communications use licensed bands below 1 GHz. The frequency band between 500 MHz and 1 GHz is the best choice for long-distance communication because the actual size and efficiency of the antenna are quite advantageous.
LoRaWAN uses free unlicensed bands and is an asynchronous communication protocol that is optimal for battery power and low cost. The LoRa and LoRaWAN protocols have unique features in handling interference, network overlap, scalability, etc., but do not provide quality of service (QoS) like cellular protocols. It is reported that the licensed Sub-GHz band auction has a price of more than US$500 million per MHz. Cellular networks and NB-IoT do not provide the same battery life as LoRa due to quality of service (QoS) considerations. Due to QoS and high frequency band usage fees, it is necessary to ensure that the QoS application scenario recommends the use of cellular networks and NB-IoT, while low cost and large number of connections are the preferred choices, then LoRa is a good choice, as shown below.
Battery Life and Downstream Delay
The idea of ​​cellular network design is to optimize the utilization of the frequency band, which in turn sacrifices node costs and battery life. On the contrary, LoRaWAN nodes are born for low cost and long battery life, and there is a certain deficiency in frequency band utilization. There are two important factors regarding battery life that need to be considered, the current consumption of the node (peak current and average current) and the protocol content. LoRaWAN is an asynchronous ALOHA-based protocol, that is, nodes can sleep for a long or short time depending on the requirements of specific application scenarios, and nodes such as cellular synchronization protocols must be networked regularly. For example, the current mobile phone on the market must be synchronized with the network every 1.5 seconds. In NB-IoT, this synchronization is less but it is still on a regular basis, which extra consumes battery power. Modulation in cellular networks is an effective way to make full use of the frequency band, but this is not effective from a node point of view. Cellular modulation (OFDM or FDMA) requires a linear transmitter to generate a modulated signal, and a linear transmitter requires a peak current several orders of magnitude more than non-linear modulation. Higher peak currents consume more battery power . However, synchronous communication protocols have advantages in terms of shorter downlink delays, while NB-IoT can provide fast data transmission rates for applications that require large amounts of data throughput. However, Class B of LoRaWAN shortens the delay of downlink communication by periodically (programming) waking up the terminal to receive downlink messages. Therefore, NB-IoT may be a better choice for applications that require frequent communications, shorter delays, or larger data volumes, but for scenarios that require lower costs, higher battery life, and less frequent communications. It's better to say LoRa.
Network coverage and deployment schedule
The essential requirement for node work is network coverage. A clear advantage for NB-IoT is that it can provide network deployment by upgrading existing network infrastructure, but this upgrade is limited to certain specific 4G/LTE base stations, and Higher costs. And this upgrade is only suitable for urban areas that already have 4G/LTE coverage, and is not suitable for remote or suburban areas without 4G coverage. The NB-IoT standard was announced in June 16 and it is expected that the module will be released in mass production in the first half of 17 years. In addition to network deployment, the corresponding commercialization and establishment of the industrial chain will take more time and efforts to explore, but will market demand and opportunities wait? LoRa's entire industry chain is relatively mature and its products are in a state of ready-made. At the same time, many countries in the world are either completing or have completed nationwide network deployments. A prominent advantage of the LoRa industry chain is that each member of the industry chain is autonomous, and some large companies are planning to create a hybrid business model to deploy networks and applications. However, the NB-IoT industry chain will be limited by frequency bands and operators.
Equipment Cost, Network Cost and Hybrid Model
For end nodes, the LoRaWAN protocol is simpler than NB-IoT, easier to develop and better for microprocessors. The modulation mechanism and protocol of NB-IoT are more complex, which requires more complicated circuits and more expenses. At the same time, NB-IoT and 3GPP are subject to taxation. At this stage, the tax on a mobile phone is about 5 US dollars, but this is too expensive for IoT devices, and if the rash of taxes and fees will cause confusion in mobile phone and other mobile communication market prices. Therefore, how the 3GPP organization weighs the taxes and fees between IoT and mobile communications is also a big problem. The low-cost and relatively mature technology of the LoRa module can already be found in the market, and the upgrade version will follow. The lack of too much copyright and tax restrictions in the LoRa Alliance makes it very impressive to have a module under the LoRa industry chain below $4. The price of LoRa modules on the market is generally in the range of 7-10 US dollars, but with the maturity of the technology, the increase of 4-5 US dollars is not a big problem. Now the price of an LTE module is hardly less than $20. Compared to the traditional network of relying solely on the “Towerâ€, deployments for IoT and LPWAN require different models to reduce expenditures and operating costs. LoRaWAN deployment is less expensive because it can be done using traditional signal towers, industrial base stations, or even portable home gateways. At this stage, a tower-type base station costs about 1,000 US dollars, an industrial base station price is less than 500 US dollars, and a home-style gateway only needs about 100 US dollars. However, for NB-IoT, the conservative price of upgrading existing 4G LTE base stations is estimated to be no less than $15,000 each.
Application examples
As mentioned earlier, there is no single technology that can meet all the needs of IoT applications at the same time. The following will use several specific application examples to analyze the applicable scenarios of NB-IoT and LoRa.
A smart meter
Companies and departments involved in the field of smart meters require high-speed data transmission, frequent communications, and low latency. Since the meter is powered by the power supply, there is no need for ultra-low power consumption and long battery life. And it also needs real-time monitoring of the line network in order to detect hidden troubles and deal with them in time. LoRaWAN ClassC can achieve low latency, but for high transmission rates and frequent communication needs NB-IoT is more suitable for smart meter selection. In addition, electric meters are generally installed at a fixed location in densely populated areas. Therefore, it is easier for the operator network.
For agriculture, low-power and low-cost sensors are urgently needed. The application of sensors such as temperature and humidity, carbon dioxide, and salinity is of great importance for agriculture to increase production and reduce the consumption of water resources. These sensors need to regularly upload data. LoRa is very suitable for such scenes. And many remote farms or arable land do not cover cellular networks, let alone 4G/LTE, so NB-IoT is not as suitable for smart agriculture as LoRa.

C automated manufacturing
The operation of factory machines requires real-time monitoring, which not only ensures production efficiency but also improves manual efficiency through remote monitoring. In the factory's automated manufacturing and production, there are many different types of sensors and devices. Some scenarios require frequent communication and ensure good quality of service (QoS). At this time, NB-IoT is a more appropriate choice. While some scenarios require low-cost sensors with low-power and long-life batteries to track devices and monitor status, LoRa is a reasonable choice. So for the diversity of automated manufacturing, both NB-IoT and LoRa are in use.
D Intelligent Building
For the reconstruction of the building, adding sensors such as temperature and humidity, safety, harmful gas, and water flow monitoring and uploading the monitored information at regular intervals facilitate the supervision of the manager and make it more convenient for the user. In general, the communication of these sensors does not need to be particularly frequent or guarantee a particularly good service quality, while a portable home gateway can meet the needs. So LoRa is a more appropriate choice for this scenario.

E Retail Terminal (POS)
Retail terminal (POS) systems often require more frequent and high quality communications, and these devices often have specialized power supplies, so there is no requirement for longer battery life. At the same time, the timeliness and low latency of communication are high. So for the above considerations NB-IoT is more suitable for this application.

F Logistics tracking
An important requirement for tracking or positioning the market is the battery life of the terminal. Logistics tracking can be a practical example of a hybrid deployment. Logistics companies can use the site network according to the needs of positioning, and can be warehouses or transport vehicles. At this time, portable base stations will come in handy. LoRa can provide such a deployment solution, and for NB-IoT, it is a big problem to track the deployment of too large base stations. At the same time, LoRa has a feature that the communication is more stable with respect to NB-IoT when moving at high speed. For the above considerations, LoRa is more suitable for logistics tracking.

to sum up
There is no undisputed choice in the IoT space. Each application scenario has its own unique needs and considerations. This article describes the respective characteristics and business models of NB-IoT and LoRa, and believes that both will have a place in the IoT market.
GPS Trackers, Locators for People, Kids.
Features that already exist
âš« Tracking: It sends GPS (Location, speed) information to your application server with configurable report interval (moving or stationary).
âš« Voice Communication
âš« Geofence: It supports circle and polygon setting.
âš« SOS Button: Makes an SOS call or SMS message to a pre-configured phone.
âš« Mileage: Reports trip start, trip end and the mileage.
âš« 3-Axis Accelerometer: Using embedded accelerometer and carefully designed algorithm to detect the trip start/stop with accuracy.
âš« Battery Low Warning: When battery level is low, it will send low-battery alarm message.
âš« Cell-ID Based Location: Device reports cell-ID based location information if GPS signal is not available.
âš« Waterproof Case: IP65 waterproof.
âš« OTA (Over the Air): The device`s configuration, setting and firmware can be remotely upgraded.
âš« Mixed-mode: It will support 1-day-1-report mode, 1-hour check mode, power saving mode, super power saving mode, fix distance mode, fix interval mode and tracking mode to optimize the use of battery.
âš« WIFI-positioning: It will support WIFI feature for positioning.
âš« Multi-Platform: Customers can get device information through APP and web platform.
Other functions can be customized
LTE Personal GPS trackers,4G Personal GPS Tracker ,Personal GPS Trackers,Personal GPS Tracker
eSky wireless Inc , https://www.eskygpsiot.com