Introduction to Circuit Domain and Packet Domain Video Telephony System
With the development of modern communication technologies, mobile multimedia communication has become a new business need. Among them, the mobile multimedia videophone service realizes the comprehensive processing of various media such as audio, video, data (text, graphic, etc.), so that users in different locations can perform real-time audio and video communication, and more and more People are concerned. According to the actual development of 3G mobile network, the conditions for developing videophone services are already available. Hong Kong and Huang have launched the WCDMAWCDMA circuit domain videophone service, and South Korea's SKT has launched the EV-DO packet domain videophone service.
1. WCDMA/TD-SCDMA circuit domain videophone
The mobile videophone service provides any combination of real-time video, audio or data media formats on WCDMA/TD-SCDMA circuit-switched wireless networks, mainly using WCDMA/TD-SCDMA networks to realize wireless intercommunication of videophones on mobile devices. So that mobile users can interact with real-time audio, video, etc. anytime, anywhere. At this stage, it may be limited to interworking between mobile terminals, and may be extended to interworking between mobile terminals and various network devices such as PSTN and ISDN.
In the WCDMA/TD-SCDMA system, since the current videophone service is implemented as a bearer service of the circuit domain, the rate can only reach 56 kb/s/64 kb/s in the RDI/UDI mode. Lower transmission rate affects its audio and video coding
The choice of the code protocol determines that it is not possible to use a large rate coding method for mobile videophone systems.
1.1 Business function
The videophone should include the following modules: video input and output and codec module, audio input and output and codec module, user data application function module, multiplexing function module, system control module, and so on. The roles of each module are as follows:
â—†Video input and output and codec module: encode and decode the input video stream data according to a specific protocol. The data collected from the video input device such as the camera is encoded and compressed into a code rate suitable for transmission under low speed conditions; at the same time, the video data decomposed by the H.223 demultiplexing layer is decoded, and then transmitted to the corresponding video. Process the device for display or other processing. Video coding protocols for WCDMA/TD-SCDMA circuit domain video telephony services are mainly H.263 and MPEG-4.
â—† Audio input and output and codec module: The main function of this module is to encode and decode the input audio data. The audio signal from an audio collection device such as a microphone is encoded and compressed, and then the encoded stream data is transmitted to the AL2 layer of H.223. At the same time, the audio data solved by the H.223 demultiplexing module is decoded, and the decoded data is transmitted to a corresponding sound processing device, such as an earpiece, a speaker, and the like. The audio coding protocols used for WCDMA/TD-SCDMA circuit domain video telephony services mainly include AMR and G723.1.
User Data Application Function Module: A typical user data application is T.120. This protocol supports multipoint data conferencing including data and image delivery, as well as data applications such as shared whiteboards and applications.
â—†Multiplication function module: multiplexes the video code stream, audio code stream, data information and control information represented by the encoded logical channel into a single output code stream, and decomposes the received code stream into various multimedia streams. The code stream, the multiplexing protocol for the WCDMA/TD-SCDMA circuit domain video telephony service, adopts the ITU-T H.223 protocol.
â—† System control module: mainly to ensure the normal establishment, release and provide information control during the videophone session, such as master-slave decision between terminals, capability exchange, logical channel opening and closing. In the WCDMA/TD-SCDMA circuit domain video telephony service, ITU-T H.245 is adopted as the control protocol.
The specific position of each module in the whole system and the composition of the entire WCDMA/TD-SCDMA circuit domain videophone system are shown in Figure 1:
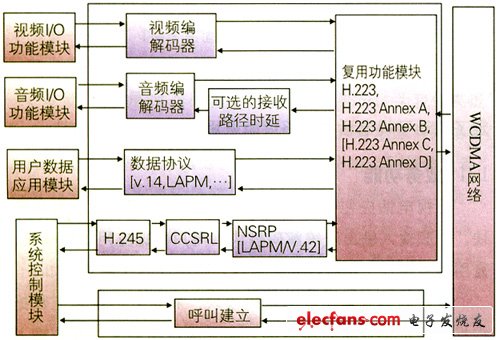
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the functional structure of the WCDMA/TD-SCDMA circuit domain videophone system
1.2 Business model
In the following, two WCDMA/TD-SCDMA circuit domain videophone terminals are all within the PLMN coverage domain, and the service model of the videophone service is briefly introduced. The videophone service is implemented as a bearer service of the circuit domain. Two mobile phones that have selected the videophone service mode establish a CS connection through the originating UTRAN, the GSTN, and the receiving UTRAN, and the videophone service data is transparently transmitted between the 3G-324M terminals. The business model is shown in Figure 2:
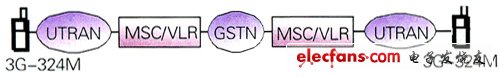
Figure 2 WCDMA/TD-SCDMA circuit domain video telephony service model
4 Port USb Charging
Ready to travel. The cable puts the charger on the table and extends to the distance from the power socket, and a travel adapter with foldable sales immediately turns it into a portable travel charger. This 4 -port USB charger has more protection safety systems to ensure the complete protection of you and your device. The mobile phone has its own charging circuit, which will be a adaptive current. No matter how much the power is, the phone can be charged safely.
4Port Usb Charger,Multi-Port Usb Charger,Flat 4 Port Usb Charger,Wall Outlet 4 Usb Plugs
shenzhen ns-idae technology co.,ltd , https://www.szbestchargers.com